Epub 2020 Nov 1. The full chlorine device has a membrane-free design and is based on an aqueous electrolyte made of sodium chloride (NaCl) which uses chlorine (Cl2/Cl) redox couple as the active material for the positive electrode. The challenge is decoding what is reality and what is just a lofty goal. Your email address will not be published. A detailed analysis of the concentration density plots indicates that the normal operation of the battery is interrupted when reactant depletion is achieved near the negative electrode both during charge and discharge. This site needs JavaScript to work properly.
The Cl2/Cl redox reaction in the aqueous NaCl electrolyte was evaluated in a concentric cell with a porous carbon coated with ruthenium(IV) oxide and titanium oxide (RuO2-TiO2), which is intended at promoting the oxidation kinetics of chloride. Winsberg J, Hagemann T, Janoschka T, Hager MD, Schubert US. Finally, are flow batteries better for long-duration applications (>6 h)? Wang C, Lu W, Lai Q, Xu P, Zhang H, Li X. Adv Mater. Like Li-ion batteries, within and between each category, flow batteries have different chemistries, including the most commonly used vanadium, and less frequently used zinc-bromine, polysulfide-bromine, iron-chromium, and iron-iron. It appears that in some cases, yes, they do, so long as they are designed and operated in a way that minimizes other contributors to degradation (but many more years of data is needed to prove this definitively). Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer. Ion-exchange membrane is known to be the most expensive cell component which dominates 40% of total cell cost. 2020 Dec;32(49):e2005036. As an added consideration and touched upon above, not all flow battery technology is equal. Modelling of a RFB that uses two immiscible electrolytes. Interestingly, the system proved effective for solving the challenging issues. The present work constitutes the first modelling attempt that simultaneously solves the fluid dynamical system formed by the two immiscible electrolytes and the electrochemical problem that determines the response of the membrane-less battery. Whether it is reviewing performance history, design details, company leadership, or financials, DNV is well positioned to help identify risks and navigate design considerations to make the best-informed decision about this nascent technology. This paper presents a membrane-less hybrid organic-inorganic flow battery based on the low-cost elements zinc (
Flow batteries have simpler monitoring and controls and less degradation than Li-ion batteries because no cell-to-cell or stack-to-stack balancing is required. pv magazine offers daily updates of the latest photovoltaics news. Notice, Smithsonian Terms of Required fields are marked *. Conclusion However, managing all the liquid electrolyte is much more difficult in flow batteries and if not contained properly will leak, which is not common in Li-ion systems. Nidec ASI New Project in Northern Ireland, New Battery Energy Storage System for Turtle Island Beach Resort, Brill Powering its Way to Making Batteries Smarter, Longer Lasting Sodium-Ion Batteries on the Horizon, Graphene Market & 2D Materials Assessment 2023-2033, Battery Swapping for Electric Vehicles 2022-2032: Technology, Players and Forecasts, Electric Vehicles: Land, Sea & Air 2022-2042, European Collaboration on Innovative Membrane-less Redox Flow Battery, Redox Flow Batteries 2020-2030: Forecasts, Challenges, Opportunities. Published by Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2021.08.020. doi: 10.3791/53235. During his Ph.D. study, he was involved as a student researcher in many research projects of fuel cells funded by US government and industries. Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) was also added through the working electrode and the electrolyte. PMC Campbell PG, Worsley MA, Hiszpanski AM, Baumann TF, Biener J. J Vis Exp. It was observed for the first time in this research that the membrane-less system exhibited significantly enhanced durability and stability as compared to the conventional membrane-based system. The capital cost of conventional redox flow batteries is relatively high (>USD 200/kWh) due to the use of expensive active materials and ion-exchange membranes. The values, according to the academics, represent the best performance for a flow battery system in the past ten 10 years. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 16(1), 011005. Then we will see if there is proof to support these claims. Half-cell charge-discharge and dissolution experiments indicate that the negative electrode reaction is limiting due to the presence of chemical side reactions on the electrode surface. Secondly, immiscible electrolytes in different phases were applied to completely resolve the intermixing issue. In this configuration, the analysis of the far downstream solution indicates that the interface remains stable in all the parameter range covered by this study. Before Your email address will not be published. Also, certain chemistries require electrolyte conditioning, a process of balancing the electrolyte chemistry using additional hardware or maintenance steps, which is required daily in many flow battery systems. Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy. Flow battery manufacturers claim that throughput-dependent degradation is very low, giving flow batteries a distinct advantage over Li-ion batteries that degrade more rapidly. Read on for an overview of the technology as it stands today, and how flow batteries key differentiators may help or hinder wider-spread adoption in the expanding energy storage market. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 70 (2017) 506518.pdf, Cyclable membraneless redox flow batteries based on immiscible liquid electrolytes: Demonstration with all-iron redox chemistry, Progress in redox flow batteries, remaining challenges and their applications in energy storage, Engineering aspects of the design, construction and performance of modular redox flow batteries for energy storage, Miniaturized biological and electrochemical fuel cells: challenges and applications, Mass transport and active area of porous Pt/Ti electrodes for the Zn-Ce redox flow battery determined from limiting current measurements, Redox flow batteries for hybrid electric vehicles: progress and challenges, Pressure Drop through Platinized Titanium Porous Electrodes for Cerium-Based Redox Flow Batteries, Development of the all-vanadium redox flow battery for energy storage: a review of technological, financial and policy aspects, Electrochemical energy storage for green grid, Electrochemical redox processes involving soluble cerium species, State of the art of all-Vanadium Redox Flow Battery: A Research Opportunities, The development of ZnCe hybrid redox flow batteries for energy storage and their continuing challenges, Progress and perspectives in micro direct methanol fuel cell, All-vanadium dual circuit redox flow battery for renewable hydrogen generation and desulfurisation, Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries with Different Electrodes and Membranes, The continued development of reticulated vitreous carbon as a versatile electrode material: Structure, properties and applications, Fabrication of microfluidic devices with application to membraneless fuel cells, Design and development of unit cell and system for vanadium redox flow batteries (V-RFB), Capital Cost Sensitivity Analysis of an All-Vanadium Redox-Flow Battery, Prospects of applying ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents for renewable energy storage by means of redox flow batteries, Planar and three-dimensional microfluidic fuel cell architectures based on graphite rod electrodes, Redox Flow Batteries for large scale energy storage, Redox flow batteries for the storage of renewable energy: A review, Integrated microfluidic power generation and cooling for bright silicon MPSoCs, Fe/V redox flow battery electrolyte investigation and optimization, Study and characterization of positive electrolytes for application in the aqueous all-copper redox flow battery, Scholar Commons A New Class of Solid Oxide Metal-Air Redox Batteries for Advanced Stationary Energy Storage, The potential of non-aqueous redox flow batteries as fast-charging capable energy storage solutions: demonstration with an ironchromium acetylacetonate chemistry, Improved fuel utilization in microfluidic fuel cells: A computational study, The importance of cell geometry and electrolyte properties to the cell potential of Zn-Ce hybrid flow batteries, A dynamic performance model for redox-flow batteries involving soluble species, A Dynamic Unit Cell Model for the All-Vanadium Flow Battery, Renewable hydrogen generation from a dual-circuit redox flow battery, Preparation of a cost-effective, scalable and energy efficient all-copper redox flow battery, EnErgy StoragE rESEarch in SwitzErland thE SccEr hEat & ElEctricity StoragE Redox Flow Batteries, Hydrogen and Distributed Storage, Microfluidic fuel cell based on laminar flow, Non-isothermal modelling of the all-vanadium redox flow battery, Vanadium: a transition-metal for Sustainable Energy Storing in Redox Flow Batteries, A Novel Regenerative Hydrogen Cerium Fuel Cell for Energy Storage Applications, Recent Advances in Enzymatic Fuel Cells: Experiments and Modeling, Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems, Nonaqueous vanadium acetylacetonate electrolyte for redox flow batteries, Journal of Power Sources 342 (2017) 371-381.pdf, High-performance microfluidic vanadium redox fuel cell, Influence of solvents on species crossover and capacity decay in non-aqueous vanadium redox flow batteries: Characterization of acetonitrile and 1, 3 dioxolane solvent mixture. Flow Battery Overview 2021 The Authors. The .gov means its official.
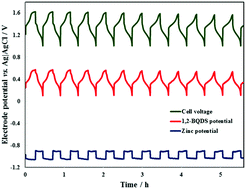
. doi: 10.1002/adma.201904690. To understand underlying physics, they developed a physics-based mathematical model to investigate the electrochemical behavior of the reactants during the system operation. This behavior is attributed to the constant and stable ohmic properties for the membrane-less system, whereas contamination or fouling by cation was found serious in the membrane-based system, causing unstable ohmic properties. Ke X , Prahl JM , Alexander JID , Wainright JS , Zawodzinski TA , Savinell RF . Mass market introduction of redox flow batteries has been hampered by various factors - material cost, limited catalyst lifetime, membrane costs, system complexity and safety issues. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled. 
Sitemap 17

