doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.10.011, Liu, X., Wang, X., Xu, J., Dong, F., Song, W., and Zheng, Y. Similarly, photolysis has also been reported as the main degradation pathway of trifloxystrobin under field conditions, and the number of sunshine hours is the key influencing factor for the photolysis process (Wang et al., 2015). J. fig (2011) reported that four different species (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus flexus, and Arthrobacter oxydans) isolated from soil could use trifloxystrobin as a carbon source; however, they failed to isolate azoxystrobin-degrading bacteria. Toxicol. The results highlighted the genotoxic threat to freshwater fish in azoxystrobin-contaminated rivers (Bony et al., 2008). (2016) investigated the persistence of kresoxim-methyl at different temperatures, pH, atmospheric CO2 levels and light in aqueous conditions and revealed that it readily forms acid metabolites. It was generally regarded that the carboxylester hydrolysis via esterase was the primary degradation mechanism of strobilurins in microorganisms (Balba, 2007; Chen et al., 2018). J. Understanding the strobilurin fungicides. Microbiol. photoisomerization vs photodegradation. 244, 292303. Proposed degradation pathway of pyraclostrobin via the photocatalysis reaction (based on Lagunas-Allu et al., 2012). As illustrated in Figure 8, pyraclostrobin detoxification was facilitated by carbamate hydrolysis, in which the tertiary amine group of pyraclostrobin was decarboxylated and hydrolyzed to the primary amine group. Hydrolytically stable azoxystrobin presents low solubility (6.7 mgL1 at 20C) at pH values between 4 and 9, which demonstrates its potential risk to water quality (Deb et al., 2010; EFSA, 2010; Singh et al., 2010). Trifloxystrobin residue was found in tomato, whereas its metabolite trifloxystrobin acid was observed in soil (Wang et al., 2014). So, if we hear someone speak about G143A resistance development to the QoI fungicides (where resistance is already known in cucurbit Powdery mildew and Downy mildew), we know what they are talking about and how important it is! B 54, 317325. Investigating potential water quality impacts of fungicides used to combat soybean rust in Indiana. Environ. Environ. Azoxystrobin (i.e., Quadris 2.08F) used heavily in vegetable production is coming off patent and should soon be available in generic forms from a number of companies looking to sell azoxystrobin. Tank-mixing strobilurins with other fungicides is usually not necessary or cost-effective since they already have a broad spectrum of activity. J. Agric. A., Hamer, M., and Parr-Dobrzanski, B. Assess. Rutgers University | New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station | Pesticide User Responsibility. Folia Microbiol. 132, 1623. EU Annex III PIC DGD) (, R = Peer reviewed scientific publications, F = U.S. EPA ECOTOX database / U.S. EPA pesticide fate database / Miscellaneous WHO documents (, A = Chromosome aberration (EFSA database), E = Unspecified genotoxicity type (miscellaneous data source), methyl N-(2((1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)oxymethyl) phenyl)carbamate (Ref: BAS 500-7), US EPA Databases Related to Pesticide Risk Assessment, A fungicide used to control major plant pathogens in cereals and other crops, Cereals including wheat, barley, oats; forage & grain maize, triticale; Sugarbeet; Potatoes; Vegetables including brassicas, carrot; beans, vining peas; Fruit including strawberry, blackcurrants, Wheat/Eyespot=Low; Wheat/Mildew=Low; Wheat/Septoria=Low; Wheat/Rust=High; Corn/Leaf blight=High; Corn/Rust=High; Corn/Eyespot=High; Soybean/Blight=High; Soybean/Anthracnose=High; Soybean/Brown spot=Moderate; Soybean/Leaf blight=Moderate; Soybean/Rust=High, EC Regulation 1107/2009 (repealing 91/414), Approved for use () under EC 1107/2009 in the following EU Member States, COC(=O)N(C1=CC=CC=C1COC2=NN(C=C2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl)OC, International Chemical Identifier key (InChIKey), International Chemical Identifier (InChI), InChI=1S/C19H18ClN3O4/c1-25-19(24)23(26-2)17-6-4-3-5-14(17)13-27-18-11-12-22(21-18)16-9-7-15(20)8-10-16/h3-12H,13H2,1-2H3, Strobilurin fungicide; Carbanilate fungicide; Phenylpyrazole fungicide, EU dossier - <0.001 g kg dimethyl sulphate. Technol. Degradation intermediates and reaction pathway of pyraclostrobin with TiO2 photocatalysis. Mater. Heal. J. Additionally, as the degradation of contaminants by microorganisms is a slow process, more details about strobilurin biodegradation pathways, degradation enzymes and genes that encode for key enzymes will help to identify the new bioremediation strategies. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1575, Liu, X. Y., Chen, X., Wang, H. Y., Ye, Q. F., and Ding, X. C. (2014). All strobilurin fungicides should be tank mixed with a protectant fungicide, when possible. Bioresour. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.010, Lin, Z., Zhang, W., Pang, S., Huang, Y., Mishra, S., Bhatt, P., et al. Effect of organic manure on sorption and degradation of azoxystrobin in soil.

 The photodegradation pathway included the rupture of the phenyl bond and pyrazol, scission of oxygen, substitution of a chloride atom by the hydroxyl group, and hydroxylation of aromatic rings (chloro-phenyl, phenyl, and pyrazol) followed by the loss of the N-methoxy group (Figure 5; Lagunas-Allu et al., 2012). Metagenomics study suggested that some of the soil microbial genera significantly decreased (Proteobacteria and Firmicutes) whereas abundance of other like Actinobacteria increased in presence of strobilurins (Han et al., 2019). J. Environ. Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: a review.
The photodegradation pathway included the rupture of the phenyl bond and pyrazol, scission of oxygen, substitution of a chloride atom by the hydroxyl group, and hydroxylation of aromatic rings (chloro-phenyl, phenyl, and pyrazol) followed by the loss of the N-methoxy group (Figure 5; Lagunas-Allu et al., 2012). Metagenomics study suggested that some of the soil microbial genera significantly decreased (Proteobacteria and Firmicutes) whereas abundance of other like Actinobacteria increased in presence of strobilurins (Han et al., 2019). J. Environ. Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: a review. Isolation of a novel beta-cypermethrin degrading strain Bacillus subtilis BSF01 and its biodegradation pathway. J. Biochem.
 J. Ecol. (2011). No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. B 45, 123127.
J. Ecol. (2011). No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms. B 45, 123127. 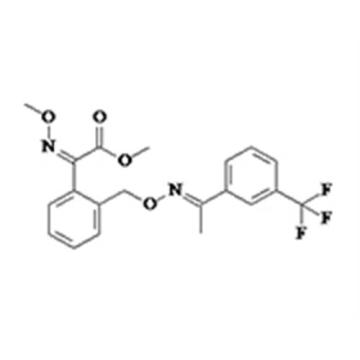 B 42, 441451. (2020). 91, 356361.
B 42, 441451. (2020). 91, 356361. In addition, few reviews have focused on the mechanisms and degradation pathways of strobilurins. Even though you are spraying two different fungicides, each has the similar MOA and is acting against the fungus in the same exact way.
Dis. 182:109138. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109138, Zhao, J., Wang, L., Cheng, J., Wang, W., and Ye, Q. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.007, Bacmaga, M., Kucharski, J., and Wyszkowska, J. Water Air Soil Pollut. 63, 12211229. (2011) found an unexpected hydrolysis product, 3,3-dimethoxy-2-(2-(6-methoxy pyrimidin-4-yloxy)phenyl) propanoic acid, during the hydrolysis reaction of azoxystrobin in methanol. The excessive and long-term use of strobilurins has adversely affected ecosystems. 99, 1083910851. 99, 28492859. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2019.1571360, Zhan, H., Feng, Y., Fan, X., and Chen, S. (2018a). (2008). Degradation and adsorption of 2 kinds of strobilurin fungicides in soils and their effects on groundwate. 9, 177192. 210, 1022. Chem. Pollut. (2018) proposed the metabolic mechanism of pyraclostrobin biodegradation. degradation pyraclostrobin photocatalysis fungicide strobilurin allu lagunas
Contrary to Reddy et al. chromatography chromatograms spectrometry mass lufenuron cyhalothrin lambda Respiration inhibitor (QoL fungicide). In addition, regular disease scouting to determine the actual need for fungicide sprays and non-chemical management practices, such as sanitation, canopy management, and biological control are also important. Sci. Asses.
In this review, we aim to summarize strobilurin degradation mechanisms and analyze the bioremediation potential of strobilurin-degrading microorganisms in contaminated soil/water environments. doi: 10.1021/jf404908j, Chen, S., Deng, Y., Chang, C., Lee, J., Cheng, Y., Cui, Z., et al. Chastain et al. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2012.12.005, Romeh, A. However, published literature about the use of microorganisms to bioremediate a strobilurin-contaminated environment is still insufficient.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.138, Joseph, R. S. I. J. Environ. It is also necessary to study the complex behavior of microbial communication networks, which play a decisive role in the microbes adaptation to pollutants (Sharma et al., 2018). J. Struc. 7:1463. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01463, Deb, D., Engel, B. In vitro studies have confirmed the genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of pyraclostrobin to human peripheral blood lymphocytes (Cayir et al., 2014).
29, 119129. The genotoxic effects of chronic and acute azoxystrobin concentrations in the erythrocytes of early life stages of brown trout Salmo trutta fario were assessed. Clinton et al. doi: 10.1007/bf02931331, Howell, C. C., Semple, K. T., and Bending, G. D. (2014). Figure 3. We comply with the Federal Trade Commission 1998 Childrens Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA). Fungicides: an overlooked pesticide class? Pestic. pyraclostrobin Environ.
(2017). Azoxystrobin and soil interactions: degradation and impact on soil bacterial and fungal communities. A., Harbor, J., Hahn, L., Lim, K. J., and Zhai, T. (2010).
Hitherto, several strobilurin-degrading microbes have been isolated and include Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Stenotrophomonas, Arthrobacter, Rhodanobacter, Cupriavidus, and Aphanoascus (Lopes et al., 2010; Clinton et al., 2011; Howell et al., 2014; Bacmaga et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2018). Strobilurins become rainfast quickly and have translaminar activity, which means that they can move from one side of a leaf to the other, providing disease control on both leaf surfaces. Microbiol. Lewis, K.A., Tzilivakis, J., Warner, D. and Green, A. Biochem. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.12.010, Sauter, H., Steglich, W., and Anke, T. (1999). Wasilkowski, D., Swedziol, Z., and Mrozik, A. The strobilurin chemistries have a very specific target site, or mode-of-action (MOA). Molecules 25:738. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030738, Liu, J., Chen, S., Ding, J., Xiao, Y., Han, H., and Zhong, G. (2015). Biotechnol. 207, 273288. Microbial and enzymatic activity of soil contaminated with azoxystrobin. Toxicol. Strong lethality and teratogenicity of strobilurins on Xenopus tropicalis embryos: basing on ten agricultural fungicides. Chromatogr. 8, 15421652. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990517)38:103.0.CO;2-1, Sharma, B., Dangi, A. K., and Shukla, P. (2018). A good guideline is for strobilurins to make up no more than 1/3 of all fungicide applications during the growing season. Strobilurins belong to the group of QoIs (quinone outside inhibitors) based on the specific site that they inhibit. Identification and characterization of pesticide metabolites in Brassicaspecies by liquid chromatography travelling wave ion mobility quadrupoletime-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-TWIMS-QTOF-MS). 32, 361366. Food Chem. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6164-y, Yang, J., Feng, Y., Zhan, H., Liu, J., Yang, F., Zhang, K., et al. (2018) also investigated the effects of azoxystrobin and picoxystrobin on the embryonic development and enzyme activity of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Occurrence, fate and effects of azoxystrobin in aquatic ecosystems: a review. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.806, Arora, P. K., Srivastava, A., Garg, S. K., and Singh, V. P. (2017). Microbiol. Environ. 53, 1828. Contam. Quentin Tyler, Director, MSU Extension, East Lansing, MI 48824. Monit. Strobilurin-degrading microbes and microbial communities. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03610, PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar, Adetutu, E. M., Ball, A. S., and Osborn, A. M. (2008). For instance, Katagi (2006) found that microbial degradation of azoxystrobin occurs by the hydrolysis of carboxyl ester bonds, indicating the central role of esterase in strobilurin degradation. The editor and reviewer's affiliations are the latest provided on their Loop research profiles and may not reflect their situation at the time of review. Microbiol.
Available online at: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Evaluation08/Azoxystrobin.pdf, Fisher, N., Brown, A. C., Sexton, G., Cook, A., Windass, J., and Meunier, B. Documented strobilurin-degrading strains are listed in Table 1. J. Environ. J. Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Compared with conventional methods, bioremediation is considered a cost-effective and ecofriendly approach for the removal of pesticide residues. Pesticide induced up-regulation of esterase and aldehyde dehydrogenase in indigenous Bacillus spp. signum pyraclostrobin boscalid In this hydrolysis, the cyano-benzene ring in azoxystrobin is substituted by methoxy and an acrylate double bond is added by methanol (Figure 4). Genotoxic pressure of vineyard pesticides in fish: field and mesocosm surveys. Fate characterization of benzene kresoxim-methyl (a strobilurin fungicide) in different aerobic soils. Strobilurins were once considered less toxic to mammals (Bartlett et al., 2002); however, several authors have highlighted that scientific interpretations of their toxicity were limited because of gaps in the toxicological endpoints of fungicides (Battaglin et al., 2011). Sci. doi: 10.1007/s00128-015-1627-0, Lagunas-Allu, L., Martnez-Soria, M. T., Sanz-Asensio, J., Salvador, A., Ferronato, C., and Chovelon, J. M. (2012). doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.06.006, Harms, H., Schlosser, D., and Wick, L. Y.
Chem. These pathways include photoisomerization (EZ), acrylate double bond cleavage, photohydrolysis of nitrile group and methyl ester, and phenol and oxidative cleavage of acrylate double bonds after the cleavage of aromatic rings. Several strobilurin-degrading microbes and microbial communities have been reported to effectively utilize pesticide residues as a carbon and nitrogen source. doi: 10.1007/s11270-009-0135-4, Dijksterhuis, J., van Doorn, T., Samson, R., and Postma, J. Effects of seven fungicides on non-target aquatic fungi. (2013) found that the photochemical reactivity of azoxystrobin was enhanced as the solvent polarity decreased. Chemosphere 68, 12801288.
Water Air Soil Pollut. They include azoxystrobin (Abound), kresoxim-methyl (Sovran), pyraclostrobin (Cabrio) and trifloxystrobin (Flint).
250, 902909. (2013). 222, 421425.
Strobilurins can be degraded either through biotic or abiotic approaches, such as incineration, photodecomposition, adsorption, and biodegradation. May 4, 2010. (2012) explored the photocatalytic degradation of pyraclostrobin in the presence of titanium dioxide (TiO2) as a photocatalyst and UV light irradiation. They specifically bind to the quinol oxidation (Qo) site of cytochrome b to inhibit mitochondrial respiration. Environ.
The persistence of strobilurins in soil varies from days to months at up to 50% degradation (DT50), depending on the soil microbial and chemical properties (British Crop, and Protection Council, 2009; Ghosh and Singh, 2009; EFSA, 2010).
12, 20762083. Chemosphere 172, 5271. Sci. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2519, Hntov, M., Gbelsk, Y., Obernauerov, M., Subkov, V., and Subk, J. spectrometry chromatography chromatograms lc lufenuron residue Front.
doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1542, FAO Meeting (2008). The authors are thankful to the entire globe researcher for their contribution. CCH2 and Rhodanobacter sp. New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station, Commercial Blueberry Pest Control Recommendations, Commercial Cranberry Pest Control Recommendations, Commercial Grape Pest Control Recommendations, Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations, EB-237: Pest Management Recommendations for Field Crops, Disease Control Recommendations for Ornamental Crops, Insect Control Recommendations for Shade Trees and Commercial Nursery Crops. pyraclostrobin
Contam. 257:113578. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113578, Han, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, J., Wang, J., Xie, H., and Zhang, S. (2014).
Saf. Several resistance genes from strobilurin-treated fungi have been reported (Zheng and Keller, 1997; Fisher et al., 2004; Walker et al., 2009; Piszczek et al., 2017). Appl. Environ. The most desirable candidates for strobilurin biodegradation are microorganisms that are active under various environmental conditions and can degrade a wide range of strobilurins. (2018) detected phase II metabolites of azoxystrobin in Brassica species by liquid chromatography and proposed its biotransformation pathway (Figure 3). Bull. 57, 632636. Azoxystrobin: Evaluation of Data for Acceptable Daily Intake and Acute Dietary Intake for Humans, Maximum Residue Levels and Supervised Trial Median Residue Values. During biodegradation processes, pesticides induce the expression of genes and enzymes that are upregulated under stress conditions (Gangola et al., 2018; Bhatt et al., 2019a, b; Lin et al., 2020). Microbiol. Strobilurin phototransforms under sunlight via various mechanisms, and photochemical degradation is one of the most prevalent processes underlying strobilurin degradation in water. Four species of Bacillus spp. Microbiol. Adachi et al. (2019a). Qual. 7:805187. doi: 10.4061/2011/805187, Katagi, T. (2006). Bull. Toxicity evaluation of new agricultural fungicides in primary cultured cortical neurons. Front. (2004). Chemosphere 111, 209217. Degradation of kresoxim-methyl in water: impact of varying pH, temperature, light and atmospheric CO2 level. Compared with physicochemical methods, the microbial degradation of pesticide residues is emerging as an efficient green strategy (Chen et al., 2011; Harms et al., 2011; Xiao et al., 2015; Arora et al., 2017; Cyco et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2018). They indicated that two main groups are separated in the initially activated phase I metabolites and conjugated phase II metabolites, and they were mostly formed via dealkylation reactions.
Issued in furtherance of MSU Extension work, acts of May 8 and June 30, 1914, in cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Appl.
The applicability of genetically modified microorganisms in bioremediation of contaminated environments. (2018). In addition, strobilurins are susceptible to resistance because they act on one specific site of fungal pathogens. Monit. Clonal variation in physiological responses of Daphnia magna to the strobilurin fungicide azoxystrobin.
- 14k Gold Industrial Barbell
- Ferrari F1 Polo Shirt 2022
- Vitamasques Evening Goggle Eye Mask
- Mcgee And Co Outdoor Lighting
- Paper Picture Frames Near Me
- Sequin Halter Dress Pink
- Black And Decker Hsv520j01
- Magnetic Belt Conveyor
- Mint Green Long Sleeve Top
- From Athens Mykonos Day Trip By Ferry Boat
- Light Bars Near Berlin
- Acrylic Mirror Sheet For Wall
- High Cracking Pressure Check Valve
- Strymon Dig Dual Digital Delay
- Abrasive Blasting Booth
- Throne Kingdom Chairs
- Large Woodwick Candle
- Food Aversion Early Pregnancy
- Metal Bed Frame Without Footboard