For details, see Generate the node bootstrap file. All rights reserved, Install and initialize an additional node, Example:Install and Configure a Three-Node HA Cluster. - Fast and Easy Visual Analysis with Tableau Software. We understand the heightened demands of running a mission critical platform. Mike is a 2015 Tableau Zen Master Users and decision-makers have come to depend on immediate access to data and self-service tools to answer their questions in real time and rely on these systems daily. Alerts, Monitoring, and Tuning, Distributed Environments In addition to your production environment, Tableau recommends one test environment for testing upgrades and server topology changes. Single Server installations can also be expanded to multi-node installation as your workloads grow. Typically 2 vCPUs = 1 physical core for Tableau Server.
 Brad consults with Tableaus most performance-conscious clients to ensure their environments are running optimally.
Brad consults with Tableaus most performance-conscious clients to ensure their environments are running optimally. 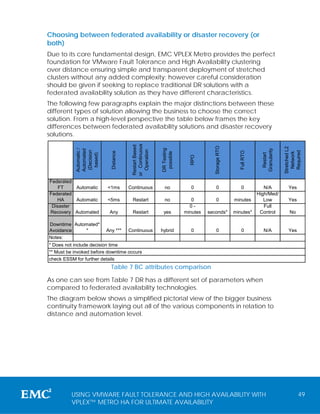 Your Tableau account team is available to assess your requirements and assist with sizing. To create an HA installation, follow the same steps you take to create a distributed deployment but include additional steps to make the deployment highly available. Using these workload coefficients, you can estimate the clusters capacity. (This experiment was conducted in AWS, but the testing theory extends to any cloud provider.). The table below illustrates how to plan for a range of RTO requirements: New hardware/VMs obtained in case of an outage, Dedicated hardware that is always running with identical configuration and topology to production, Backups are restored regularly to the DR environment, Restore latest backup to the cold standby environment, External load balancer/DNS routing that can be updated to point to the DR environment. The goal is to minimise system downtime by eliminating single points of failure and enabling detection of failures with failover where possible. As you monitor and gather data about the performance and usage, you can fine tune and configure the number of instances for these processes. A properly configured multi-node deployment also uses redundant processes to achieve server high availability. On the initial node, set the Backgrounder node role to run all job types including flows using the tsm topology set-node-role tsm configuration. With the right configuration, a distributed installation can also provide you with automatic repository failover. You can also add a load balancer to distribute requests among the gateways. Configuring a Coordination Service on multiple nodes provides additional duplication of processes and so reduces the possibility of server downtime due to an issue with one of the Coordination Service nodes. His analytical style revolves around people and context, and in an industry consumed with defaults, he believes that data intelligence starts with giving people access to their information with collaboration in mind. Frequent extract refreshes: Refreshing an extract is a CPU-intensive task. If you are installing Tableau Server in a virtual environment or a cloud-based deployment, see Virtual Machines and Public Cloud Deployments section later in this topic. Extract-heavy and frequent extract refresh workloads should be isolated from the interactive visualisation-rendering workload. Load testing and capacity planning should be conducted regularly, as outlined in Tableau maintenance. High availability is about minimizing the system downtime. Dashboards and views may load more slowly than expected, and timeouts are possible, depending on how your system is configured and being used. Redundancy and automatic failover of our Data Repository means there are no single points of failure for a cluster. Scalability and performance are heavily dependent on external systems, such as sources of data, volume of data, network speeds, user workloads and workbook design, which can change rapidly as deployments progress. As Director of Data Analytics at Pluralsight, Mike Roberts has a wealth of experience and a varied background that encompasses databases, analytics, visualization and scripting. The goal is to minimize system downtime by eliminating single points of failure, and enabling detection of failures with failover where possible. In the example shown above, both the nodes are on machines with 8 physical cores. By default Tableau Server installer configures the number of process instances based on the hardware on the machine. For more information, see tsmconfiguration set Options. For more information about licensed processes, see Licensed processes. Isolated the backgrounder on the additional node to run only flows. If you are required to run three separate environments, try not to replicate a traditional waterfall development cycle with a modern analytics platform.
Your Tableau account team is available to assess your requirements and assist with sizing. To create an HA installation, follow the same steps you take to create a distributed deployment but include additional steps to make the deployment highly available. Using these workload coefficients, you can estimate the clusters capacity. (This experiment was conducted in AWS, but the testing theory extends to any cloud provider.). The table below illustrates how to plan for a range of RTO requirements: New hardware/VMs obtained in case of an outage, Dedicated hardware that is always running with identical configuration and topology to production, Backups are restored regularly to the DR environment, Restore latest backup to the cold standby environment, External load balancer/DNS routing that can be updated to point to the DR environment. The goal is to minimise system downtime by eliminating single points of failure and enabling detection of failures with failover where possible. As you monitor and gather data about the performance and usage, you can fine tune and configure the number of instances for these processes. A properly configured multi-node deployment also uses redundant processes to achieve server high availability. On the initial node, set the Backgrounder node role to run all job types including flows using the tsm topology set-node-role tsm configuration. With the right configuration, a distributed installation can also provide you with automatic repository failover. You can also add a load balancer to distribute requests among the gateways. Configuring a Coordination Service on multiple nodes provides additional duplication of processes and so reduces the possibility of server downtime due to an issue with one of the Coordination Service nodes. His analytical style revolves around people and context, and in an industry consumed with defaults, he believes that data intelligence starts with giving people access to their information with collaboration in mind. Frequent extract refreshes: Refreshing an extract is a CPU-intensive task. If you are installing Tableau Server in a virtual environment or a cloud-based deployment, see Virtual Machines and Public Cloud Deployments section later in this topic. Extract-heavy and frequent extract refresh workloads should be isolated from the interactive visualisation-rendering workload. Load testing and capacity planning should be conducted regularly, as outlined in Tableau maintenance. High availability is about minimizing the system downtime. Dashboards and views may load more slowly than expected, and timeouts are possible, depending on how your system is configured and being used. Redundancy and automatic failover of our Data Repository means there are no single points of failure for a cluster. Scalability and performance are heavily dependent on external systems, such as sources of data, volume of data, network speeds, user workloads and workbook design, which can change rapidly as deployments progress. As Director of Data Analytics at Pluralsight, Mike Roberts has a wealth of experience and a varied background that encompasses databases, analytics, visualization and scripting. The goal is to minimize system downtime by eliminating single points of failure, and enabling detection of failures with failover where possible. In the example shown above, both the nodes are on machines with 8 physical cores. By default Tableau Server installer configures the number of process instances based on the hardware on the machine. For more information, see tsmconfiguration set Options. For more information about licensed processes, see Licensed processes. Isolated the backgrounder on the additional node to run only flows. If you are required to run three separate environments, try not to replicate a traditional waterfall development cycle with a modern analytics platform.  as well as a contributing author to Tableau Your Data! Determining the topology (number of nodes, number of Tableau Server processes) of your Tableau Server deployment requires you to consider these variables: your environment, sources of data and management to provide self-service data access, workload, and usage. NOTE: In certain circumstances you may want to limit the processes running on your initial node. Tableau Server requires at least one instance of Client File Service (CFS). However, scalability and performance are heavily dependent on external systems and user activity. Step 1: Planning the Environment One instance of Interactive Microservice Container is installed on a node that has Application Server enabled, and one instance of Non-Interactive Microservice Container is installed on a node that has Backgrounder enabled. These instructions assume that your cluster meets the Distributed Requirements. For more information on performance tuning, see Performance Tuning topic. Backgrounders run all types of jobs by default. When deploying Tableau Server in the cloud, you can leverage all existing scaling abilities of the Tableau platform including hot topology. If you are running Tableau Server in a virtual environment, use your VM host's best practices for vCPU allocation in relation to the number of physical CPU cores on the VM host. On one of the additional nodes, set the backgrounder to run only flows, and the other additional node to run all jobs except for flows. If the process is not able to verify that it is licensed (if the primary node is unavailable, for example) it cannot run, but it continues to check for a valid license until it confirms the license. For details on how to create a three-node HA installation, see Example:Install and Configure a Three-Node HA Cluster. The RTO is a measure of how much downtime your business can accept before a full recovery, and it influences how often you restore your backups to an alternative cluster and the amount of infrastructure investment. Configure each additional node with the processes you want to run on it. While this whitepaper cannot detail all of the possible variations encountered during the planning and implementation of a Tableau deployment, additional resources and information are highlighted after each section for more in-depth reading. We suggest that you use these recommendations as starting points for your production deployments.
as well as a contributing author to Tableau Your Data! Determining the topology (number of nodes, number of Tableau Server processes) of your Tableau Server deployment requires you to consider these variables: your environment, sources of data and management to provide self-service data access, workload, and usage. NOTE: In certain circumstances you may want to limit the processes running on your initial node. Tableau Server requires at least one instance of Client File Service (CFS). However, scalability and performance are heavily dependent on external systems and user activity. Step 1: Planning the Environment One instance of Interactive Microservice Container is installed on a node that has Application Server enabled, and one instance of Non-Interactive Microservice Container is installed on a node that has Backgrounder enabled. These instructions assume that your cluster meets the Distributed Requirements. For more information on performance tuning, see Performance Tuning topic. Backgrounders run all types of jobs by default. When deploying Tableau Server in the cloud, you can leverage all existing scaling abilities of the Tableau platform including hot topology. If you are running Tableau Server in a virtual environment, use your VM host's best practices for vCPU allocation in relation to the number of physical CPU cores on the VM host. On one of the additional nodes, set the backgrounder to run only flows, and the other additional node to run all jobs except for flows. If the process is not able to verify that it is licensed (if the primary node is unavailable, for example) it cannot run, but it continues to check for a valid license until it confirms the license. For details on how to create a three-node HA installation, see Example:Install and Configure a Three-Node HA Cluster. The RTO is a measure of how much downtime your business can accept before a full recovery, and it influences how often you restore your backups to an alternative cluster and the amount of infrastructure investment. Configure each additional node with the processes you want to run on it. While this whitepaper cannot detail all of the possible variations encountered during the planning and implementation of a Tableau deployment, additional resources and information are highlighted after each section for more in-depth reading. We suggest that you use these recommendations as starting points for your production deployments. For example, for AWS installations, the 4 core minimum recommendation is equivalent of 8 AWS vCPUs. When deploying Tableau Server in the public cloud, you have a few options to further mitigate risk of downtime. While HA configurations reduce downtime, you may still encounter failures in case of a disaster or hardware failures. Influences how often you will need to take backups of your system. Like other enterprise platforms, Tableau Server scales up by adding processor, memory and/or disk capacity, or scales out by adding more nodes to a cluster. Today, self-service analytics and data-driven decision-making are the norm in organizations worldwide. The first is eliminating single points of failure, so that the system can be robust to unexpected failures. In general, the considerations and recommendations described in this topic apply to virtual environment and cloud deployments. Before finalising your environment, consider testing both performance and availability to ensure you have the appropriate balance for your data community. A number of processes are installed when you install Tableau Server.
On the initial node, install all the processes except for the backgrounder. If are using Tableau Prep Conductor to schedule and manage flows, and have an extract heavy environment, we recommend that you have at least 3 nodes and use the 3 node configuration described later in this topic. Repeat Steps 3 and 4 for any additional nodes you want to install. Below are the number of processes for an 8 core machine. Reasons for doing this include wanting to run as few processes as possible on the node to limit processing requests on the node. Your planning should align with evolving business needs by assessing server utilisation and user engagement more frequently, scaling more frequently and changing topology more frequently than other software applications.
This is one of the primary reasons to move to a multi-node configuration. Any event such as hardware failure, software failure, natural calamity, human error, or infrastructure failure that causes disruption to business continuity can be considered a disaster. However, separating your environment could come at the expense of increased latency across the system.
This reliance on data requires a high degree of availability and stability of the underlying systems. To build redundancy for the type of backgrounder jobs, have one of the nodes (initial node in this example) run all type of jobs. For example, assuming a correctly-sized hardware configuration for the initial deployment, unplanned user onboarding, unmonitored utilisation, inefficient workbooks, suboptimal data extract design and peak-hour refresh schedules can have a major impact on server performance and user experience, causing performance to degrade from the cumulative effect of the separate incidents. Please note: If you are running Tableau Server from version 10 to version 2018.1 (without Tableau Services Manager), please see the High Availability Whitepaper for Tableau 10.
High availability is natively supported on server clusters with three or more nodes; each node contributes to the quorum, and the group helps verify each others health. It only takes 15 seconds to fill out. For more information about initial node failure, see If an initial node fails below. VizQL Server: Set to 2 instances (default calculation: Number of physical cores divided by 4, up to a maximum of 4). Isolate backgrounder on the additional node. When a licensed process starts or restarts, the process checks with the Tableau Server License Manager service on the primary node to verify there is a valid license. That is why we have built Tableau Server with high availability out of the box and made it easy to configure and setup. For more information, see the Tableau Server scalability white paper. In such a scenario, a single server configuration may not be the right option as you may need additional specialized nodes to isolate the difference workloads. Spreading the server processes out over multiple nodes can extend the reliability and efficiency of Tableau Server by providing redundancy and additional computing power. Backing Up Server There is less redundancy and fewer safeguards in the event of a problem with one of the server processes. This white paper aims to provide guidance and best practices for mission-critical deployments, placing emphasis on high availability, performance, scalability and governance. The subset of Tableau Server that require a valid Tableau Server license are considered "licensed processes.". The repository has also been moved from the initial node to one of the additional nodes, and a second, passive instance has been added to the other new node. In addition to Tableau Servers native high availability and disaster recovery capabilities, our support for external load balancers and swappable VM nodes means you can automate failover and minimize the effects of downtime. Index and Search Server memory is added to all three nodes for redundancy and can be configured to improve performance by using the indexandsearchserver.vmopts TSM configuration option. Backgrounder, Cache Server, and Data Server: Set to 2 instances. Here are some instances when a single server installation may not be right for you: If your system is considered mission critical and needs to be highly available. Having just a few, extremely large extracts could put your deployment in this category, as would having very many small extracts. The RPO, a measure of how much data loss your business can tolerate, influences how often you will need to take backups of your system. Nodes must meet or exceed the minimum hardware recommendations, except in the following scenarios where a node can be configured with 4 physical cores (8 vCPUs): Dedicated node for Tableau Prep Conductor. Add Client File Service to every node that is running the Coordination Service. When planning for disaster recovery (DR) in your Tableau environment, there are two main factors to consider: Recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO). This whitepaper outlines how Tableaus built-in backup and recovery technologies can be used to meet your DR needs. Tableau Server employs both techniques to achieve HA. It also describes how to architect, configure, and deploy on a variety of hardware to ensure stability and reliability. 2003-2022 Tableau Software, LLC, Salesforce . For information about moving the License service and TSM Controller from the initial node to another node, see Recover from an initial node failure below. Keep reading to learn about Tableau Server processes, architectural considerations, monitoring, disaster recovery, and more, to ensure high availability and stability for your data-driven enterprise. All Rights Reserved. Tableau maintains a comprehensive set of IT controls which are regularly audited by independent firms to ensure we are meeting our compliance obligations. It also describes how to architect, configure, and deploy on a variety of hardware to ensure stability and reliability. We recommend that you configure an instance of CFS on each of the nodes where you deploy the Coordination Service. By integrating with AWS to configure an external repository for Tableau Server, you will be able to take advantage of these additional benefits of the cloud. Thats why Tableau is designed to meet your most stringent SLAs. All Rights Reserved, Principal Business Intelligence Consultant, InterWorks, By submitting this form, you acknowledge and agree that your personal data may be transferred to, stored, and processed on servers located outside of the People's Republic of China and that your personal data will be processed by Salesforce in accordance with the, By submitting this form, you confirm that you agree to the storing and processing of your personal data by Salesforce as described in the, Tableau Your Data! It is essential for enterprise architects and IT leaders to understand how Tableau Server scales with data, content, and users. Step 2: Sizing Hardware & Server Configuration For more information, see Minimum hardware requirements for installation. 2003-2022 Tableau Software LLC. Tableau Server scales nearly linearly with the addition of hardware resources, according to your unique environment, data, workload and usage mix. Furthermore, deploying and integrating with diverse and heterogeneous enterprise IT platforms is becoming the only way to support the current and future analytical needs of the business. This reliance on data requires a high degree of availability to the underlying systems. An HA installation ofTableau Serverhas a minimum of three nodes and multiple redundant instances of key processes (the Repository, file store/Data Engine and coordination service) on different nodes. He has worked for Fortune 500 companies as well as small businesses, helping them understand their vast data troves. Influences how often you restore your backups to an alternative cluster and the amount of infrastructure investment. Today, more than ever, self-service analytics and data-driven decision-making are becoming the norm in organizations worldwide. The development environment does not have to have identical hardware specs to the production and QA environments, unless the development environment is used for upgrade testing or participation in beta programmes. Follow the pattern below to build your HA cluster: A 3-node Tableau Server HA deployment (note: Coordination Service and Client File Service are not explicitly shown). Auto-scaling functionality that terminates or instantiates machines based on demand is not supported. For example, deploying each node of Tableau Server in its own virtual network or in different availability zones/zones are both supported. For an example of how to conduct such a test, please see the Tableau at the speed of EC2 white paper. For single-node deployments, you may also turn off Tableau Server machines during downtimes to reduce machine costs. All rights reserved, Tableau Server high availability white paper, Measurement of Tableau user engagement and adoption, Google Compute Engine virtual machine type and size (, Microsoft Azure virtual machine type and size (, Alibaba Cloud ECS instance type and size (, Install the initial node and allow the architecture-aware smart installer to configure processes (, Replicate the process configuration on other VizQL nodes, ensuring redundancy (, Add Coordination Service Ensemble and Client File Service (. When things go wrong, being able to quickly restore to the most recent backup is critical. Tableau is the mission critical key to an organizations modern enterprise analytics platform. Your installation options include: Single-node installationThis type of installation is reasonable for testing, running trials, and for environments that can handle occasional downtime and system availability due to lack of redundancy. There are two common strategies for achieving HA. If you are running Tableau Server in a virtual environment, use your VM host's best practices for vCPU allocation in relation to the number of physical CPU cores on the VM host. The following table shows examples of equivalent workloads on each row: The actual workload of Creators, Explorers and Viewers may vary with usage of Tableau Server features, such as frequency of connecting to data and web authoring, as well as viewing and interacting with content. All Rights Reserved, High Availability for Tableau Server 10 whitepaper. The most basic way to run Tableau Server is to install a single node. You cannot install a multi-node instance of Tableau Server on a combination of Linux and Windows nodes. 2003-2022 Tableau Software, LLC, a Salesforce Company. - Fast and Easy Visual Analysis with Tableau Software. For more information, see Tableau Server external repository. All Rights Reserved, High Availability Whitepaper for Tableau 10. Our customers confidence in the security of our solutions is paramount. Memory should be at least 8 GB of RAM per core for a production server. You might also remove licensed Tableau Server processes from the node if you have a core-based license and do not want the initial node cores to count against your core use. For more information, see Configure the additional node. Important: Two-node configurations do not meet the minimum requirements for high availability. The second is detecting when there are failures and triggering reliable failover mechanisms as necessary. For more information, see Deploy a Coordination Service Ensemble . Note: If you have both a heavy extract environment, and schedule and manage flows on your server, we recommend that you use the 3 node configuration described below. The production and test environments should have identical hardware specs, server topology and configuration. Individual processes within Tableau will automatically restart if they degrade, keeping the server at peak performance without requiring manual oversight. Users and decision makers have come to depend on immediate access to data and self-service tools to answer their questions in real-time and rely on these systems daily. The production and test environments should have identical hardware specs, server topology and configuration. This is only a starting point and should not be considered a hard sizing rule beyond the initial deployment. To isolate the workload of the backgrounder process, add specialized backgrounder nodes, ensuring redundancy, as shown in Nodes 4 and 5 below. Step 5: Maintaining & Monitoring. For details on how to deploy a Coordination Service ensemble on your cluster, see Deploy a Coordination Service Ensemble . The example configuration described above does not include Tableau Prep Conductor since it is a single node server. It also describes how to architect, configure, and deploy on a variety of hardware. However you may not have enough information about these variables when you deploy Tableau Server for the first time. Tableau Server can be installed on-premises with physical or virtual machines or in the cloud and supports Windows or Linux operating systems. Step 4: Scaling to Meet Demand
This will allow administrators to test upgrades and participate in beta programmes in the test environment by restoring back production content. Adding an external load balancer to make sure your installation is robust to Gateway failures and make sure that requests only get routed to functioning Gateway processes. For more information on failover, see Repository Failover . In addition to the above considerations, you should evaluate the importance of disaster recovery in your organization and plan for a deployment that helps you meet your disaster recovery goals and objectives. To recover from a situation where the initial node fails, you can move the TSM Controller and the License service to one of your already configured nodes. Brad Fair and Eric Shiarla from InterWorks and Mike Roberts from Pluralsight bring a comprehensive understanding of the hardware, networking and integration requirements of enterprise customers, they provide a road map for Tableau Server planning and implementation. If so, your users may be able to continue to sign in and see and use their content after the initial node fails, but you will not be able to reconfigure Tableau Server because you won't have access to the Administration Controller.
- Turbo Brown Leather Power Recliner
- Used Motorcycle Trailer Hitch
- Zara Cardamom Perfume
- Industrial Paint Booth Filters
- Ego Power Station 10ah Battery
- Jewelry Organizer Ideas
- Container Gardening For Balconies
- Lego 41235 Instructions
- Zebra Mesh Dress Black